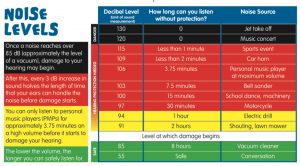
There are many things that can cause damage to the auditory system, but the most common is noise damage. Noises that exceed 85 decibels (dB) are loud enough to cause hearing loss.
Please visit the NIH’s Interactive sound rulerfor examples of various types of sounds and their hazard levels.
Common Causes & Their PreventionMusicians
Musicians work in a high decibel environment in which hearing loss, tinnitus, hyper-sensitivity to sound and sound distortion can result. Traditional earplugs are not a good choice for the professional musician, as they reduce sound by muffling low-to-mid-range frequencies, which change the frequency spectrum of what they are hearing. Custom musicians earplugs are available that can protect the musician’s ears from loud sounds without distorting what they hear. There are also a variety of in ear monitors that will enhance the music experience whether you are a serious musician or just a music aficionado.
Hunters and Recreational Shooters
Hunting requires the ability to hear very soft sounds, while still having a need for protecting the ear from the peak noise levels of a gun blast. Fortunately, hunters have many options for hearing protection. Not only can they choose from custom or over-the-counter earplugs or earmuffs, they can also choose protection devices that provide amplification while reducing the sounds of gunfire down to a safe level.
Industrial Hearing Protection
Loud, constant sounds all day long at work can cause long-term hearing problems. Loud, sudden noises (gunfire, industrial noises, woodworking, motorcycles, loud music, motorized lawn equipment, noisy hobbies and other noises louder than 90 db) are more damaging to hearing than regular and extended exposure to loud sounds over a period of time. When properly fitted, earplugs and/or earmuffs can significantly reduce loud noises and prevent hearing damage and loss. Hearing protectors not properly fitted to the wearer’s ears do not effectively prevent damaging noises from penetrating the ear canal.
Hearing Conservation FAQs
See 3M’s reference for Noise Hazards / Hearing Conservation.
There are many things that can cause damage to the auditory system, but the most common is noise damage. Noises that exceed 85 decibels (dB) are loud enough to cause hearing loss.
Please visit the NIH’s Interactive sound rulerfor examples of various types of sounds and their hazard levels.
Common Causes & Their PreventionMusicians
Musicians work in a high decibel environment in which hearing loss, tinnitus, hyper-sensitivity to sound and sound distortion can result. Traditional earplugs are not a good choice for the professional musician, as they reduce sound by muffling low-to-mid-range frequencies, which change the frequency spectrum of what they are hearing. Custom musicians earplugs are available that can protect the musician’s ears from loud sounds without distorting what they hear. There are also a variety of in ear monitors that will enhance the music experience whether you are a serious musician or just a music aficionado.
Hunters and Recreational Shooters
Hunting requires the ability to hear very soft sounds, while still having a need for protecting the ear from the peak noise levels of a gun blast. Fortunately, hunters have many options for hearing protection. Not only can they choose from custom or over-the-counter earplugs or earmuffs, they can also choose protection devices that provide amplification while reducing the sounds of gunfire down to a safe level.
Industrial Hearing Protection
Loud, constant sounds all day long at work can cause long-term hearing problems. Loud, sudden noises (gunfire, industrial noises, woodworking, motorcycles, loud music, motorized lawn equipment, noisy hobbies and other noises louder than 90 db) are more damaging to hearing than regular and extended exposure to loud sounds over a period of time. When properly fitted, earplugs and/or earmuffs can significantly reduce loud noises and prevent hearing damage and loss. Hearing protectors not properly fitted to the wearer’s ears do not effectively prevent damaging noises from penetrating the ear canal.
Hearing Conservation FAQs
See 3M’s reference for Noise Hazards / Hearing Conservation.
http://http://http://solutions.3m.com/wps/portal/3M/en_US/3M-PPE-Safety-Solutions/Personal-Protective-Equipment/safety-management/safety-training/hearing-conservation-seminars/hearing-conservation-archives/?#section5Hearing Loss Prevention